When running Google Ads, managing over 200 keywords is the norm, but mastering match types can make all the difference. Advertisers who fine-tune their Google Ads match types see up to 70% higher click-through rates. They can also cut wasted ad spend by limiting ad visibility to more relevant search queries. It’s not just a technical detail, it’s a smart way to boost your ROI.
From ecommerce brands targeting “winter boots” to B2B companies seeking “enterprise software” leads, your success depends on mastering keyword match types. These powerful targeting tools act as filters, determining when your ads appear based on user search queries.
In this post, we’ll cover the fundamentals of exact, phrase, and broad match types through practical examples, then show you how to automate your keyword strategy for maximum efficiency. You’ll walk away with both the knowledge and tools to optimize your campaigns at scale.
Why Expand Beyond Amazon Advertising?
Want to double your customer reach? While Amazon captures 50% of initial product searches, Google commands another 31.5%. By advertising on both platforms, you’re not just expanding your audience—you’re getting paid to do it.
Amazon’s Brand Referral Bonus program rewards sellers who drive external traffic to their listings. When you combine this with Google’s massive search volume, you’re essentially turning Google’s users into Amazon customers, all while earning bonuses for each conversion.
Here’s the smart play: optimize your Google Ads to capture that additional 32% of shoppers who start their journey outside Amazon.
You’ll boost your visibility, increase sales potential, and earn Amazon’s rewards for bringing new customers to their platform.
3 Google Ads Match Types: Starting with the Right Keyword Strategy
Broad Match, Phrase Match, and Exact Match are keyword match types that each serve different purposes, offering varying levels of reach and precision. Understanding their differences—and when to use each—can help optimize your budget and maximize ROI.
1. Exact Match
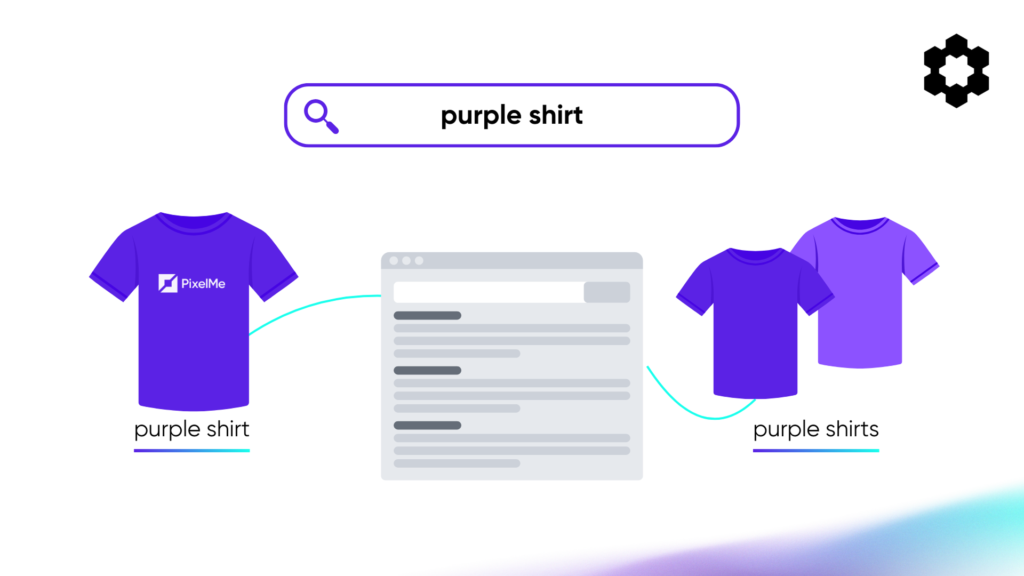
Exact Match ensures that your ads trigger only when users search for your exact keyword or close variations. This provides maximum control over search intent and audience targeting.
Example
Keyword: “purple shirt”
- Triggers: “purple shirt”, “purple shirts”
- Does NOT trigger: “best purple shirts”, “cheap purple shirt for sale”
Pros
- Highly targeted traffic from high-intent searchers
- Higher conversion rates
- Lower irrelevant clicks, leading to better cost efficiency
Cons
- Lower reach, as it excludes broader search variations
- More time-consuming keyword research to capture all relevant searches
Best Use Case
Perfect for businesses targeting ready-to-buy customers. For example, an ecommerce store selling luxury watches could use Exact Match for “Rolex Submariner” to attract buyers specifically looking for that model.
2. Phrase Match

Phrase Match triggers ads when the search query contains the keyword phrase in the same order but may include additional words before or after.
Example
Keyword: “purple shirt”
- Triggers: “buy purple shirt for men”, “best purple shirt brands”
- Does NOT trigger: “shirt purple for men”, “best shirts that are purple”
Pros
- Balances reach and relevance
- Captures mid-funnel buyers who are still researching but have strong intent
- More flexibility than Exact Match while maintaining control over audience intent
Cons
- May still trigger less relevant searches compared to Exact Match
- Requires ongoing monitoring and negative keywords to refine targeting
Best Use Case
Ideal for businesses looking to expand reach while maintaining keyword intent. For instance, a local gym might use Phrase Match for “personal trainer near me” to capture searches like “best personal trainer near me” or “certified personal trainer near me.”
3. Broad Match
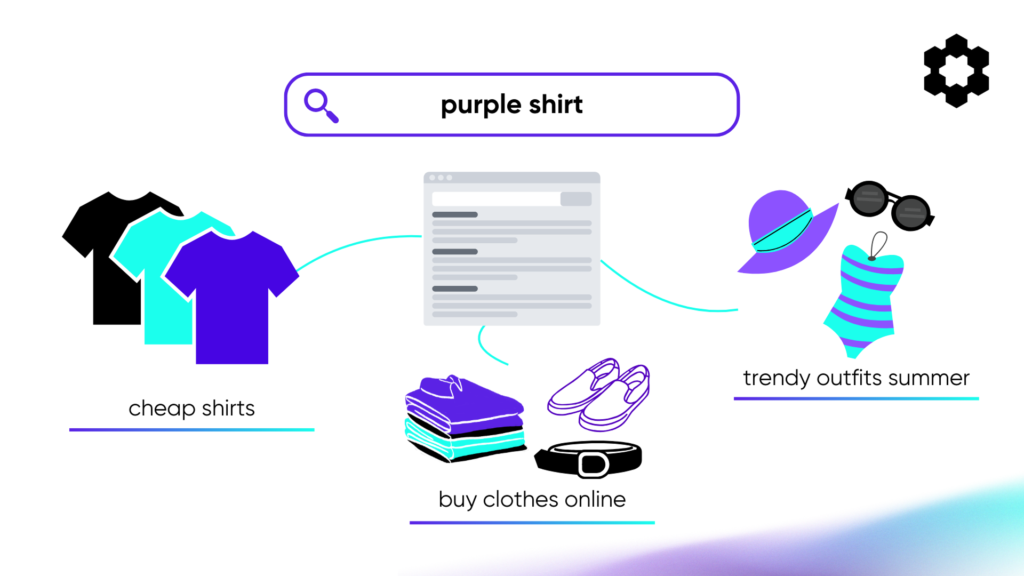
Broad Match casts the widest net, showing ads for searches related to the keyword, even if the exact words aren’t present. Google uses AI to determine relevance.
Example
Keyword: “purple shirt”
- Triggers: “cheap shirts”, “buy clothes online”, “trendy outfits summer”
- Does not trigger: (Fewer restrictions, but still attempts to maintain relevance)
Pros
- Maximum reach and exposure
- Helps discover new keyword opportunities
- Generates valuable data on user behavior
Cons
- Higher risk of irrelevant clicks and wasted ad spend
- Lower conversion rates compared to more refined match types
- Requires strong negative keyword lists to filter unwanted traffic
Best Use Case
Great for awareness campaigns and data gathering. For example, a new DTC clothing brand launching an ad for “summer dresses” might use Broad Match to find unexpected, high-converting search terms like “best dresses for summer weddings.”
Modifiers for Phrase & Broad Match
Historically, advertisers used a “+” symbol before keywords to refine Broad Match, but Google now incorporates AI-driven close variant matching.
Example
- Using “purple +shirt” (historically) meant the search must include “shirt” but could vary for “purple.”
- Today, Google considers synonyms, misspellings, and related terms automatically, and will rotate in terms depending on what is performing best.
Best Use Case
For advertisers who need a balance between reach and control, modifying keywords can help limit overly broad matches.
Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent ads from appearing in searches containing unwanted terms, reducing wasted spend on irrelevant clicks.
Example
- A luxury watch brand might add “cheap,” “discount,” or “replica” as negative keywords.
- A dentist targeting “teeth whitening” might exclude “DIY” or “home remedies.”
Pros
- Increases ad relevance
- Reduces wasted ad spend
- Improves campaign efficiency and ROI
Cons
- Requires constant monitoring and updates
Which Match Type is Best for You?
The right choice depends on your business goals:
- Use Exact Match for high-intent searches where precision is critical.
- Use Phrase Match for a balance of reach and relevance.
- Use Broad Match when exploring new keyword opportunities or launching a brand-awareness campaign.
- Use Negative Keywords to refine any campaign and improve performance.
Strategically combining these match types can help you create a well-rounded campaign that drives conversions while optimizing ad spend. Testing and ongoing refinement are key to success in Google Ads match types.
Try PixelMe’s Keyword Harvester to automatically identify top-performing keywords and optimize your match types. Transform your Google Ads efficiency by seamlessly converting broad match terms to exact match – all in one powerful tool.
Best Practices for Using Google Match Types
1. Use Broad Match As a Starting Point
As previously mentioned, broad match serves as a strategic entry point when launching an ad campaign on Google. It allows you to target several related terms and collect valuable data on search behavior before narrowing down to more refined match types.
For example, a website selling athletic shoes might start with “running shoes” in broad match. Over time, analyzing search data may reveal that “best cushioned running shoes” or “men’s trail running shoes” convert better, signaling opportunities for more targeted approaches.
2. Transition from Broad to Exact Match
Once data has been collected, the next step is refining broad match results into exact matches to focus on the highest-performing keywords.
Why Transition to Exact Match
- Optimized Ad Spend: By identifying high-converting keywords, advertisers can allocate budget more efficiently, reducing wasted ad spend on irrelevant searches.
- Enhanced Campaign Performance: Precise targeting improves click-through rates (CTR), quality scores, and return on investment.
Suppose an ecommerce brand starts with “purple shirt” in broad match. Through data analysis, they find that “purple shirt for men” consistently leads to conversions. Transitioning this phrase to exact match ensures ads are shown to highly relevant users, increasing the likelihood of sales.
Try PixelMe’s Keyword Harvester to automatically identify top-performing keywords and optimize your match types. Transform your Google Ads efficiency by seamlessly converting broad match terms to exact match – all in one powerful keyword research tool.
3. Adjust Match Types Based on Campaign Goals
Each campaign objective demands a different approach to match types:
Brand Awareness Campaigns
- Match Type: Broad Match
- Goal: Maximize reach and collect data on audience behavior.
- Example: A new eco-friendly sneaker brand may use broad match with “sustainable shoes” to discover how consumers search for similar products.
Lead Generation Campaigns
- Match Type: Phrase Match
- Goal: Balance reach and intent by ensuring ads appear for queries with strong interest.
- Example: A SaaS company offering marketing automation tools might use phrase match with “best email marketing software” to attract potential leads.
Sales & Conversion Campaigns
- Match Type: Exact Match
- Goal: Drive conversions by targeting high-intent users.
- Example: A luxury watch retailer may use exact match with “buy Rolex Submariner” to ensure their ad is served to users actively looking to purchase that specific model.
Testing New Markets
- Match Type: Broad & Phrase Match Combination
- Goal: Understand new customer behavior patterns.
- Example: A health supplement brand expanding into Europe may use broad and phrase match with “best vitamin D supplement” to analyze regional search trends before tweaking their Google ads match types strategy.
4. Align Keywords with Bidding Strategies
Google Ads performs best when match types align with your bidding strategy:
- Broad match + Smart Bidding allows Google’s AI to optimize ad placement based on real-time signals.
- Phrase and exact match work well with manual bidding or target impression share strategies.
5. Leverage Responsive Search Ads with Broad Match
Why? This combination increases reach, adapts to consumer behavior shifts, and improves ad relevance.
UK-based tails.com used this approach in Germany and increased sign-ups by 182%, while clicks grew by 258%.
The Role of User Intent in Keyword Selection
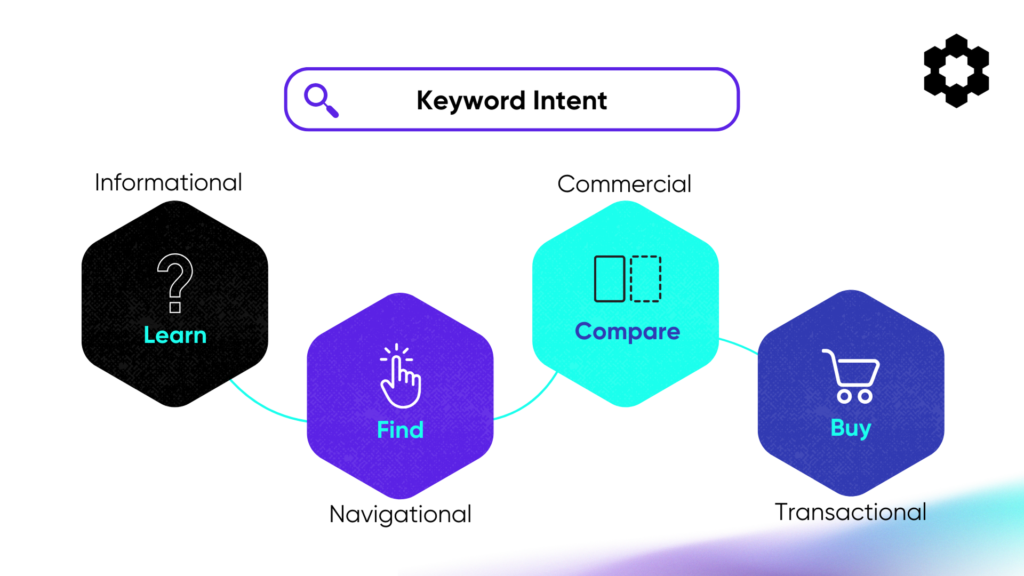
Selecting the right keywords is not just about volume and competition—it’s about aligning with user intent. Every search falls into one of four key intent categories.
1. Informational Intent
Users with informational intent are looking for answers, insights, or guidance. They may search for “how to start an Amazon FBA business” or “best practices for ecommerce listing optimization.” For these queries, broad match keywords are useful to capture a wide range of variations and ensure visibility.
2. Navigational Intent
When users already have a specific brand or website in mind, they exhibit navigational intent. Searches like “PixelMe login” or “D8aDriven by Carbon6 features” indicate they are looking for a particular destination. ‘
Here, exact match keywords are ideal to ensure your brand appears at the top of relevant searches.
3. Commercial Intent
Users in the commercial intent phase are considering a purchase but need more details before deciding. They may search for “best Amazon PPC management tools” or “Carbon6 vs. other Amazon software.”
Phrase match keywords work well here, capturing queries with intent to compare and evaluate.
4. Transactional Intent
When users are ready to buy, they perform transactional intent searches, such as “buy Amazon inventory management tool” or “SoStocked subscription pricing.”
Exact match keywords are crucial at this stage to ensure your ad appears for high-conversion searches.
Match Google Ads with User Intent
To maximize ad effectiveness, advertisers must tailor their strategies to user intent:
- Align ad copy with search intent signals: Ensure the messaging resonates with where the user is in their buying journey. If they are in the research phase, emphasize features and comparisons; if they are ready to purchase, highlight promotions and urgency.
- Use match types strategically: Broad match for discovery, phrase match for mid-funnel engagement, and exact match for high-converting queries.
- Create separate ad groups for different intent levels: This allows for better targeting, ad relevance, and budget allocation.
- Adjust bidding strategies based on intent signals: Higher bids for transactional searches, lower bids for broad informational searches to manage spend efficiently.
Customizing Keyword Performance Criteria
Setting performance thresholds ensures that advertising spend remains efficient and scalable:
- Define performance benchmarks: For example, only keeping keywords with a cost-per-click (CPC) under $2 or an Advertising Cost of Sale (ACoS) below 25%.
- Monitor and refine keywords continuously: Pause underperforming keywords and scale those meeting profitability goals.
- Adapt thresholds based on campaign goals: A brand awareness campaign may allow a higher CPC, whereas a profitability-focused campaign should have stricter ACoS limits.
Mastering Match Types for Campaign Success
Gaining a deeper understanding of Google Ads match types based on campaign goals and user intent is a game-changer for advertisers looking to optimize their PPC campaigns. By strategically using broad, phrase, and exact match types, you can capture the right audience at the right time, improving conversion rates and reducing wasted ad spend.
Rapid-Fire Strategies for Success
- Use broad match for discovery: Gather valuable search data before refining your keyword strategy.
- Transition to exact match: Focus on high-intent searches to optimize ad spend and drive conversions.
- Incorporate negative keywords: Filter out irrelevant traffic to improve campaign efficiency.
- Adjust bidding based on intent: Allocate higher bids for transactional keywords, lower bids for informational ones.
- Leverage automation tools: Use AI-driven solutions like PixelMe’s Keyword Harvester to identify top-performing keywords and streamline your match type selection.
Armed with these strategies and the right tools, you’re now ready to transform your Google Ads campaigns into highly targeted, cost-efficient marketing engines.




